Exploring the Marvels of Polymers: From Plastics to High-Tech Materials
Introduction: In our modern world, polymers are everywhere. From the plastic bottles we use daily to the advanced materials used in aerospace engineering, polymers play a crucial role in shaping our lives. But what exactly are polymers, and why are they so important? In this blog, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of polymers, exploring their structure, properties, and the myriad ways they impact our lives.
Understanding Polymers: At its core, a polymer is a large molecule composed of repeating structural units called monomers. These monomers can be simple molecules like ethylene or more complex structures like amino acids. Through a process called polymerization, these monomers link together to form long chains, giving rise to the unique properties of polymers.

Types of Polymers: Polymers can be classified into several categories based on their structure, properties, and synthesis methods. Some common types of polymers include:
- Thermoplastics: These polymers can be melted and reshaped multiple times without undergoing any significant chemical change. Examples include polyethylene, polypropylene, and polystyrene.
- Thermosets: Unlike thermoplastics, thermosets undergo irreversible chemical reactions during curing, leading to a rigid, cross-linked structure. Epoxy resins and phenolic resins are examples of thermosetting polymers.
- Elastomers: Elastomers are polymers with exceptional elasticity and resilience. Rubber, both natural and synthetic, is a prime example of an elastomer.
- Biopolymers: Derived from natural sources, biopolymers offer environmentally friendly alternatives to traditional synthetic polymers. Examples include cellulose, starch, and proteins like collagen.
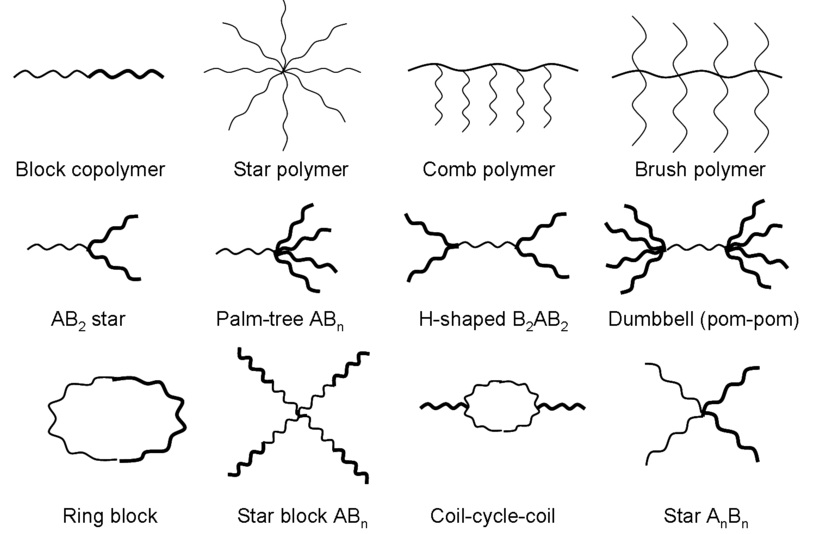
Properties and Applications: The properties of polymers vary widely depending on their chemical composition and structure. Some key properties include:
- Mechanical Strength: Polymers can range from flexible and rubbery to rigid and strong, making them suitable for a wide range of applications.
- Thermal Stability: Some polymers exhibit excellent heat resistance, making them ideal for high-temperature environments.
- Electrical Insulation: Certain polymers possess insulating properties, making them valuable in electrical and electronic applications.
- Chemical Resistance: Many polymers are resistant to chemicals, acids, and solvents, enhancing their durability in harsh environments.
The applications of polymers are virtually limitless. They are ubiquitous in everyday products such as packaging materials, textiles, and consumer goods. Additionally, polymers play crucial roles in industries like automotive, aerospace, healthcare, and electronics. For instance, advanced composite materials based on polymers are increasingly being used in aircraft and spacecraft construction due to their lightweight and high strength-to-weight ratio.

Future Perspectives: As technology advances and our understanding of materials science deepens, the potential applications of polymers continue to expand. Researchers are exploring innovative approaches to tailor the properties of polymers, such as designing self-healing materials and biodegradable polymers to address environmental concerns.
Furthermore, the emergence of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, has revolutionized the production of polymer-based components, enabling rapid prototyping and customization.
Conclusion: Polymers are truly remarkable materials that have revolutionized countless aspects of our lives. From everyday conveniences to cutting-edge innovations, polymers continue to drive progress across diverse industries. As we strive towards a more sustainable future, the development of novel polymers with enhanced properties and reduced environmental impact will undoubtedly play a pivotal role in shaping tomorrow’s world.



